Essential Fatty Acids
Are you ready to take charge of your health? Schedule your free 20-minute discovery call with our New Patient Coordinator or fill out this form to see how you can become a patient at MaxWell Clinic and start your healing journey today.
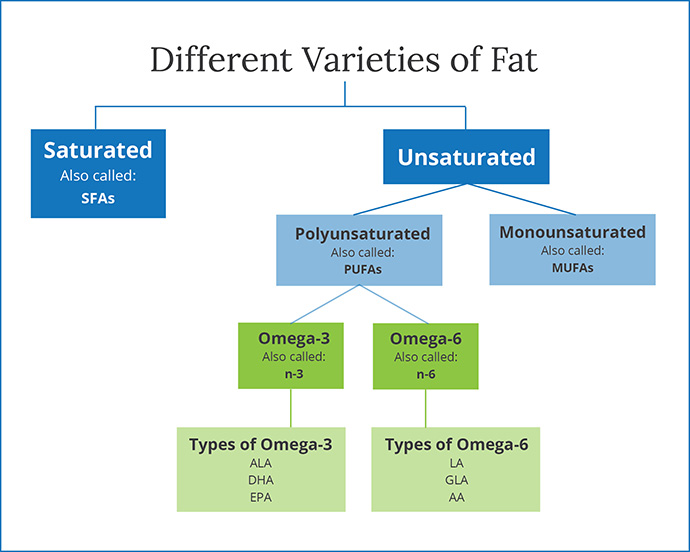
What are Essential Fatty Acids?
Essential Fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats and can be broken down into 2 different types omega-3s and omega-6s. They are known as essential because they are necessary for good health but our body cannot produce them. Omega-6 fatty acids are essential and mainly used for energy.
There are 4 types of omega-6 fats including linoleic acid (LA), arachidonic acid (AA), gamma linoleic (GLA), and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). Omega-6s can be found in sunflower oil, safflower oil, soybean, corn oil, canola oils, meats, and dairy products.
Omega-6s provide a range of benefits including:
- Helps reduce nerve pain.
- Can help reduce blood pressure
- Supports bone health
- Lowers risk of heart disease – boost protective HDL
- May help reduce symptoms of ADHD
- May help treat Rheumatoid Arthritis
Omega-6 are more commonly found in the western American diet and they can lead to proinflammatory eicosanoids. Though these eicosanoids are important chemicals in the immune system; their excess production can increase inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
There are 11 Omega-3 fatty acids but the most popular ones include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The body mostly utilizes ALA for energy and to convert to EPA and DHA. EPA and DHA help reduce inflammation, prevent blood clotting, and are crucial for brain function and development.
Some sources of ALA include walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds and flaxseed oil. EPA and DHA come from marine sources like algae, fish, and krill.
Omega-3s provide a range of benefits including:
- Support mental health – Reduces symptoms of depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and risk of psychotic disorders.
- Improve heart health – Increase HDL cholesterol and reduce blood pressure, triglycerides and arterial plaque formation
- Supports healthy weight management
- Reduce inflammation.
- Support brain development in infants
- Promote bone health
Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio
Omega-6 fatty acids like LA and AA are usually abundant in most people’s diet. While omega-3 fatty acid ALA is often consumed, conversion from ALA to EPA and then DHA is very low. Therefore it is very important to get EPA and DHA from marine sources.
While Omega-6 fatty acids still provide benefits to the body, a proportionally higher consumption of Omega-3 fatty acids can protect us against inflammatory diseases!
The current recommendation for primary cardiovascular disease prevention, at minimum, is 250 mg/day EPA + DHA (combined) or at least 2 servings of oily fish/week.
Supplement recommendation is dependent on omega-6 status, current intake of DHA and EPA, and risk factors including hypertriglyceridemia, coronary heart disease history, underlying health conditions.
Sources of EPA and DHA
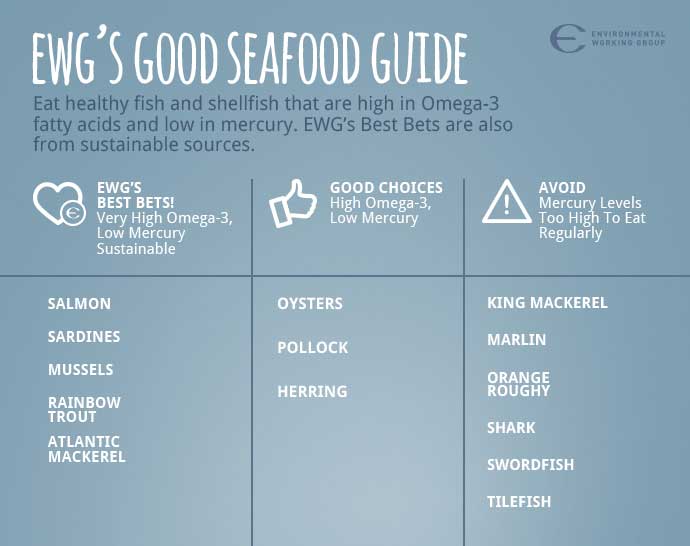
Fish and fish oils are great sources of omega-3 but there is a large concern over the amount of mercury found in fish and the effects of it on the human body.
Methylmercury is more commonly the type of mercury found in foods and can be easily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract absorbs approximately ninety five percent of ingested Mercury where it can then enter the red blood cells and the brain. Fetuses are the most at risk. Exposure to mercury can adversely affect a baby’s growing brain and nervous system.
Avoid fish that are high in mercury and when selecting fish remember the smaller the fish the better! The bigger fish eat smaller ones, the predators then absorb their prey’s contamination in a process known as biomagnification.
Some Action Items You Can Take Today!
- Eat fish high in omega-3 & are low in mercury at least 2x per week
- Have omega-3 and omega-6 levels tested
- Take omega-3 supplements as recommended by your clinician, especially if you do not eat fish.
Are you ready to take charge of your health? Schedule your free 20-minute discovery call with our New Patient Coordinator or fill out this form to see how you can become a patient at MaxWell Clinic and start your healing journey today.
References:
Bos, D.J., Oranje, B., Veerhoek, E.S., Van Diepen, R.M., Weusten, J.M., Demmelmair, H., et al. (2015) Reduced Symptoms of Inattention after Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation in Boys with and without Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology, 19 March 2015. Epub ahead of print.
Peoples GE, McLennan PL, Howe PR, Groeller H. Fish oil reduces heart rate and oxygen consumption during exercise. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;52(6):540-7. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181911913. PMID: 19034030.
Saravanan, P., Davidson, N.C., Schmidt, E.B. and Calder, P.C. (2010) Cardiovascular Effects of Marine Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Lancet, 375, 540-550. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60445-X
Disclaimer:
Feeding MaxWell nutrition blogs are produced for informational purposes only and brought to you by MaxWell Clinic, LLC. The information is provided by a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist that has been trained in providing dietary advice backed by nutritional science and research. The nutrition information is not to be construed as medical advice or medical nutrition therapy. The information is not to be used as individualized nutrition counseling or used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent any medical problems. The content of these blogs should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment from your medical provider. Any information, examples, recipes, foods, or stories presented do not constitute a warranty, guarantee, or prediction regarding the outcome of the individual using the material. The reader is responsible for working with a qualified professional before beginning any new dietary program or plan. The writers and publishers of this nutrition information are not responsible for any adverse reactions, effects, or consequences resulting from the use of provided information, recipes, foods, or suggestions.